Description:
- Resistor, restricts or limits the flow of electrons in a circuit.
- As discussed in the previous post, materials fall into two basic categories such as conductors and insulators.
- Conductors such as metals let electricity flow through them; insulator such as plastic and wood generally do not.
- But, any substance will conduct electricity if you put big enough voltage across it; even air which is normally an insulator suddenly becomes a conductor when a powerful voltage builds up in the clouds and what makes lightning.
- Rather than talking about conductors and insulators, it's better to talk about resistance, (the ease with which something will let electricity flow through it)
- A conductor has low resistance, while an insulator has much higher resistance.
- Devices called resistors, let us introduce precisely controlled amounts of resistance into electric circuits.
- Resistor is a passive electrical component with two terminals that are used for either limiting or reducing the flow of current in any particular portion of the electric circuit.
- It is also used to transform current signal into a voltage signal and vice versa.
Made up of:
- Copper wires which are coiled around a ceramic rod.
- And the outer part is coated with an insulating paint.
- A resistor doesn't have any fixed "positive or negative" terminal.
- When a current (I) flows through a circuit, the terminal through which the current enters into the resistor will be considered as positive terminal and the other one will be considered as the negative terminal.
- Otherwise, a resistor alone doesn't have any fixed positive or negative terminal.
SI Unit of Resistance is Ohm
- An Ohm is the resistance that occurs when a current of one Ampere (A) passes through resistor with a one volt (V) drop across its terminals.
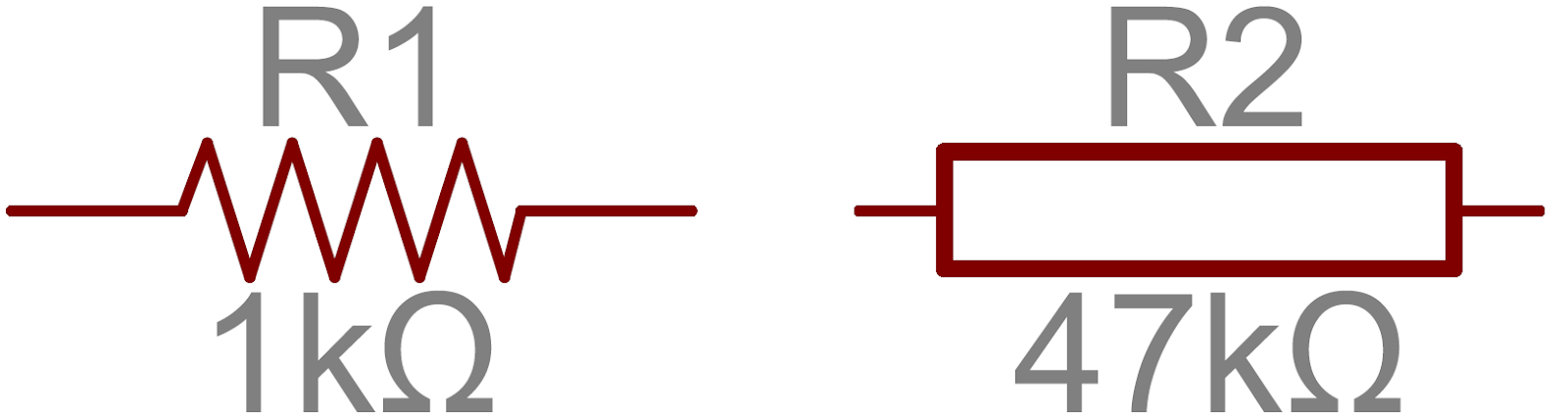
Symbol of Resister:
- Both are symbols of a fixed resistor.
- The first symbol belongs to ANSI standard and the second belongs to IEC standard.
- R1 and R2 are one kiloohm and 47 Kiloohm Resistors respectively.
- A kiloohm (kΩ) = 103 Ohms i.e., One kiloohm is equal to 1,000 ohms.
Read the next post: 6.4 Ohm's Law


Comments
Post a Comment